Thursday, January 10, 2019
Some Types of Belly That Aren't Caused by Overweight
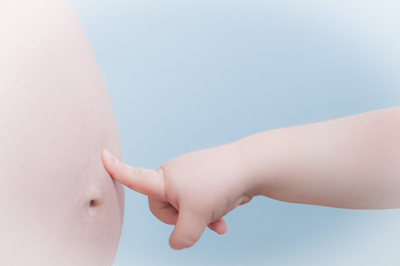
Love Handles
How does it look you have folds on your sides, and it’s usually caused by sedentary lifestyle, sweet tooth, excess alcohol consumption, lots of sugar and refined carbs cookies [cakes] and white bread or starchy carbs pasta and rice.
How to get rid of it
- drink less alcohol
Several glasses of wine drunk three to four times a week lead to a wine waist with a potbelly and fat size. Stop drinking altogether for two weeks, and then remember moderation.
- rethink your diet
Avoid special dietary products and the low-fat foods, add eggs, lean meat, and vegetables and healthy fats such as avocado, nuts and [high-fat] fish in your diet.
- find time for exercise
You don’t have to go to the gym long walks will do as well also you can perform lunges squats and reverse push-ups at home. Keep in mind that physical exercise and proper diet are enough. Both of these will reduce your belly in size and give you strength to go on.
Stress Belly
The fat is concentrated around the belly button and the belly is thick, not loose here are the factors that cause it
- chronic stress
- skipping meals
- drinking lots of coffee
- irritable bowel syndrome
- unhealthy food such as salted nuts and potato chips
No worries! There are some effective ways to get rid of it.
- go to bed early
You sleep little and poorly under stress which disrupts leptin production, a hormone that helps to regulate your appetite and metabolism. You need to sleep at least seven to eight hours every day and go to bed before midnight.
- relax before sleep
Breathing exercises, taking a bath, or meditation, all do the trick these useful habits will help you sleep well also. Limit your nightly coffee consumption; don’t drink more than two cups of coffee a day.
- don’t overexert your body with exercise
Excess Cardio only increases your cortisol levels, instead do yoga or take long walks even a gym session will calm you down but don’t overdo it.
- include magnesium in your diet
Magnesium is a relaxing mineral. You can find it in dark Green vegetables, nuts, and wheat bran. Also, do some yoga or stretching and drink chamomile tea before going to bed that will reduce cortisol and helps your body calm down.
Low Belly
How does it look? you’re slim but your lower belly protrudes a bit. You should know that it might be caused by recent motherhood, anonymous and overly exert of exercise, unchanging diet, spinal curvature.
We know some brilliant ways to get rid of it?
- a healthy diet and lots of fiber
Green leaves vegetables, whole-grain bread, and other sources of fiber are good for you, include them in your diet.
- give up on squats
You probably do them incorrectly exerting too much effort on your lower back or aggravating spinal Curvature. It makes your tummy more prominent. So you should replace squats with planks.
- perform different exercises
Don’t overexert any single part of your body; try circuit training, that way you’ll work every muscle group. Also, drink more water and go with easily digested foods such as green vegetables and light proteins such as fish and chicken.
Mommy’s Belly
After giving birth the building looks like you’re pregnant again. Why? Well, it’s caused by a few reasons.
- too little time for yourself
The uterus lowers itself after birth and achieving results becomes harder than it was before pregnancy. It will take at least six weeks to return to your normal size.
- you started training too early
It’s better to have a rest of two to three months after giving birth before taking up exercise. Don’t rush to the gym; now it’s better to spend time with your baby.
- weak muscles of the pelvis
Muscles of the pelvis like other muscles else need to be regularly trained. There are a lot of special exercises and simulators for this, just choose your favorites.
How to get rid of mommy’s belly? It’s easy when you put some effort into this
- consume healthy fat
Try to consume healthy fats every day; nuts, vegetable oil, and olives. It helped you fight fatigue. Which is a bonus for mom? Also, include fish oil in your diet
- do KEGEL exercises
They act as a natural corset for your body strain and relax the pelvic floor muscles 15 to 20 times and repeat this exercise 5 times a day the results will come very soon
- stuck in your belly
It’s a healthy habit that will tone your muscles without overexerting them; give it a try.
- give up on squats and crunches
These are the worse for your body after birth, let it recover first. Don’t forget to take afternoon naps and do stretching; before sleep, cover the windows and let yourself sleep during the day. The sleep hormones will intensify fat burning.
Inflated Belly
Your stomach is flat in the morning but grows during the day regardless of whether you have excess weight. It’s caused by food allergy, sluggish bowels, intestinal flora imbalance.
Here are easy ways to get rid of it
- exclude foods that don’t go well with your body
You should cut gluten bread pasta, alcohol, yeast cakes, and beer and process dairy products such as cheese milk, and butter out of your diet
- eat more fresh vegetables, meats, chicken, and fish
Try to avoid bread and pastries for two weeks and see if your belly stops swelling
- never skip breakfast
Make it the largest of your meals as digestion is at its peak in the morning. Don’t eat at night, chose your food thoroughly and drink a lot of water
- ad pre and probiotics in your diet Swelling may be a sign of imbalance intestinal flora premium probiotics are present in sour cream and fruit and vegetables including cabbage, garlic, and onion. Remember that a healthy stomach is a flat stomach
- breathing
Do the following exercise every morning; lie on your back, relax completely, inhale and exhale 10 times deeply.
Now you know that a big belly isn’t always caused by excess weight. Lots of reasons cause this problem and there are lots of solutions that can solve this.
Wednesday, January 9, 2019
Pleural Effusion
Pleural effusion is a common clinical problem that can complicate many medical conditions. Breathlessness is the most common symptom of pleural effusion of any cause and the most common reason for pleural drainage.
It can pose a diagnostic dilemma to the treating physician because it may be related to disorders of the lung or pleura, or to a systemic disorder. Patients most commonly present with dyspnea, initially on exertion, predominantly dry cough, and pleuritic chest pain. To treat pleural effusion appropriately, it is important to determine its etiology. However, the etiology of pleural effusion remains unclear in nearly 20% of cases.
The diagnostic evaluation of pleural effusion includes chemical and microbiological studies, as well as cytological analysis, which can provide further information about the etiology of the disease process.
The physiological mechanisms underlying breathlessness in patients with a pleural effusion are unclear and likely to be multifactorial with patient-related and effusion-related factors contributing.
Several Ways to Get Rid of a Headache
You can try this to ease your pain without meeting your doctor.
1. Try a cold pad for 15 min and repeat after 15 min of interval; It works for migraine.
2. Use a heating pad or hot compress; it's effective for tension or sinus headache.
3. Ease pressure on your scalp or head.
4. Dim the lights; lights can cause migraine even the light from your computer screen so you need to wear sunglasses outdoor.
5. Try not to chew; chewing gum can hurt not just your jaw, but your head as well.
6. Practice relaxation include yoga or meditation.
7. Drink coffee or tea; caffeine can relief your pain.
8. Massage your neck for a few minute.
Few short point to relief your headache
- Close your eyes and rest
- Massage your neck and temples
- Warm up your neck
- Relax
- Minimize stress
- What you eat and drink can have a big impact on your headaches.
Primary headache
The cause of primary headache include :
1. Migraine
- 10-20 % of the population
- Peak at 25-55 yrs
2. Tension type
- 30-78 % of the population
- Peak at 30-39 yrs
3. Trigeminal autonomic cephalalgia
- 1 %
4. Other
Criteria for diagnosis migraine
- At least 5 attacks
- 2 or more of the following
+ Unilateral
+ Pulsating
+ Moderate or severe
+ Aggravation by/or causing avoidance of routine physical activity
- 1 or more of the following
+ Nausea and/or vomiting
+ Photophobia and phonophobia
- Lasting 4-72 hours (untreated or unsuccessfully treated)
Criteria for diagnosis of tension type headache
- 2 or more of the following
+ Bilateral
+ Pressing or tightening
+ Mild to moderate
+ Not aggravation by routine activity
- Both
+ No nausea and vomiting
+ Photophobia or phonophobia
- At least 10 episodes
- 30 minutes to several days
Sunday, January 6, 2019
ACNE VULGARIS
Acne is a chronic dermatosis, frequently in adolescence and involve principle on the face. Usually it is the disorder the of the sebaceous unit, those chronic inflammatory dermatosis are presented as notable open/closed comedones, papules, pustules, or nodules.
Epidemiology
The prevalence in French is more than 70 % in adolescence [Vidal Reco 2018]. The predominant sex is male > female in adolescence but female > male in adult.
Physiopathology and etiology
There are 3 factors pathogenic involved in acne
- hypersecretion sebaceous androgenic dependent
- retention sebaceous related to hyperkeratosis of canal infundibulum follicular
- inflammation is related to colonization follicular sebaceous by Propionobacterium acnes. P. acnes promote proinflammation mediator lead to inflammation of follicle and dermis.
Genetic maybe associated in 50 % and if there exist family history, the acne may be more severe and occur earlier.
Androgens are produced by the adrenal gland, the gonads and also by the sebaceous gland, it plays in the role of the following:
- stimulating the growth and secretory function of sebaceous glands (produce sebum)
- dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate (DHEA-S)[androgen precursor] converted to testosterone via the action of several enzymes and then testosterone is converted to 5-alpha-dihydrotestosterone (DHT) via the action of type I 5-alpha reductase in the sebaceous gland.
- Both DHT and testosterone bind to receptor presented in the sebaceous glands and the outer root sheath keratinocytes of the follicular epithelium to get in its action. In this case, the men who are lacking androgen receptor do not produce sebum and do not develop acne.
Risk factors
- Overproduction of androgen can cause acne but in the majority case of acne, the androgen level is normal. The excess of androgen is presented in polycystic ovarian syndrome, congenital adrenal hyperplasia, and adrenal or ovarian tumors.
- External factor: include oily cosmetics, cocoa butter, scrubbing with soaps, detergents, and astringents may worsen the disorder by rupturing comedos, promoting the development of inflammatory lesions.
Turtlenecks, bra straps, shoulder pads, orthopedic casts, and sports helmets, hands against the skin and others may cause acne by occlusion of pilosebaceous follicles leads to the comedone formation.
- Diet: natural hormonal components of milk or other bioactive molecules in milk, ingestion of high glycemic loads could exacerbate acne. In these cases, insulin-like growth factor (IGF) may play a role in acne. There is the limitation of data about consumption of chocolate, zinc, omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, vitamin A, and dietary fiber to determine the roles in acne vulgaris.
- Stress: would be related to the severity of acne. Receptors for corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) are presented in sebaceous gland so the CRH system may participate in the occurrence of stress-exacerbated acne.
- Insulin resistance: it may increase the production of androgen and IGF.
- Obesity: rising BMI increased the risk for acne in females.
- Smoking maybe worsen the severity of acne,
Diagnosis
History: duration, medications, cleaning products, stress, smoking, exposures, diet, and family history have to be asked. Females may worsen 1 week before menses.
Physical exam: the present of closed comedones (whiteheads), open comedones (blackheads), nodules or papules, pustules (“cysts”), scaring and post inflammatory lesions: ice pick, rolling, boxcar, atrophic macules, hypertrophic, depressed, sinus tracts; in face, neck, chest, upper back, and upper arms. Usually, acne vulgaris affects those areas of the body that have the largest hormonally-responsive sebaceous glands.
Classification: there isn’t a universal classification system for acne vulgaris. American Academy of Dermatology in 1990 classified acne into 4 grads : Mild: few papules/pustules, no nodules; Moderate: some papules/pustules, few nodules; Severe: numerous papules/pustules, many nodules; and Very severe: acne conglobata, acne fulminans, acne inversa.
There are 3 types of basic lesion: hyperseborrhoea (oily appearance, greasy to the touch, predominant on the nose, forehead, cheeks and upper thoracic region), retinal lesions (comedones, micro and macro-cysts), and inflammatory lesions (papules, pustules, nodules).
Differential diagnosis Many disorders may present with acneiform eruptions which have similar features but are unrelated to acne vulgaris.
Rosacea: the feature of rosacea include erythema, telangiectasias, and papules or pustules on the central face. Acne vulgaris is the absence of telangiectasias. Acne cosmetica: caused by an irritant reaction to cosmetic ingredient; especially heavy oil-based hair products. Papules or pustules may occur within hours after the application, commonly on the forehead.
Drug-induced acne: commonly steroid, characterized by the presence of monomorphous inflammatory popular eruption.
Perioral dermatitis or periorificial dermatitis: the presence of small, grouped, erythematous papules in a perioral (or perinasal, periorbital), a rim of skin around the vermilion border of the lip.
Sebaceous hyperplasia: it is the enlargement of sebaceous glands, which umbilicated yellowish papules and found on the forehead and cheeks.
Pseudofolliculitis barbae and acne keloidalis nuchae: most common in African origin, it’s related to the configuration of the hair follicle. A foreign body inflammatory reaction caused by short shaved or clipped hairs curl back toward the skin, penetrate the skin. After lesion papule and pustule heal, it may result in keloidal scarring.
Folliculitis: there aren’t comedos, and lesions are usually monomorphous.
Keratosis pilaris: it caused by keratotic follicular plugging, characterized by the presence of small follicular papules on the extensor surfaces of the upper arm of thighs, erythema also may be present.
Favre-Racouchot syndrome: resulted from cutaneous photodamage (sun damage), characterized by open and closed comedos on the damaged area, mostly on the lateral upper cheeks and seen in middle and older aged.
Nevus comedonicus: linear arrangement comedos in childhood.
Adnexal tumors: flesh-colored facial papules seen in trichoepitheliomas, trichodiscomas or fibrofolliculomas.
Hidradenitis suppurativa: characterized by the recurrent, inflamed nodules and abscesses of intertriginous skin areas, such as the axilla, groin, perianal, perineal, and inframammary regions. The comedones, sinus tracts, and scarring also present. It is a chronic inflammation of the skin.
Steatocystoma multiplex: the presence of multiple yellow or skin-colored sebum-filled cysts on the trunk, upper arms, or chest.
Tuberous sclerosis: presented as the persistent 1 to 3 mm pink or red papules on the nose and medial cheeks.
Occupational acne or chloracne: comedos, inflammatory papules, pustules, nodules, or cysts can occur after exposure to chemicals include insoluble cutting oils, coal, hydrocarbons. The comedone are large and monomorphic, mostly affect on the face, neck, postauricular skin, axillae, and scrotum.
Tropical acne: presented large inflammatory nodule on the trunk and buttocks. It’s related to environmental temperature.
Radiation acne: radiation can induce follicular hyperkeratotic plugs.
Apert syndrome: it could be presented of an acneiform eruption on the arms, buttock, and thigh.
TREATMENT
• Comedonal (grade 1): keratinolytic agent (see as follows for specific agents)
• Mild inflammatory acne (grade 2): benzoyl peroxide or topical retinoid or benzoyl peroxide +/− topical antibiotic +/− topical retinoid
• Moderate inflammatory acne (grade 3): Add systemic antibiotic to grade 2 regimen.
• Severe inflammatory acne (grade 4): as in grade 3, or isotretinoin
• Topical retinoid plus a topical antimicrobial agent is first-line treatment for more than mild disease.
• Topical retinoid + antibiotic (topical or PO) is better than either alone for mild/moderate acne.
• Topical retinoids are first-line agents for maintenance. Avoid long-term antibiotics for maintenance.
• Avoid topical antibiotics as monotherapy.
• Recommended vehicle type
– Dry or sensitive skin: cream, lotion, or ointment
– Oily skin, humid weather: gel, solution, or wash
– Hair-bearing areas: lotion, hydrogel, or foam
• Apply topical agents to entire affected area, not just visible lesions.
• Mild soap daily to control oiliness; avoid abrasives.
• Avoid drying agents with keratinolytic agents.
• Gentle cleanser and noncomedogenic moisturizer help decrease irritation.
• Oil-free, noncomedogenic sunscreens
• Stress management if acne flares with stress
Source :
UpToDate 2018
Vidal Recos 2018
5-Minute Clinical Consult 2018
Famous Funny Commercials
This is the ten of the most funny commercials that made me laugh and that are also famous, that have written history so to say. I hope you e...